how to read ir spectroscopy graph Spectroscopy infrared ftir interpreting pictorial interpretation nmr memorize chimie college analyse proton
Ready to become an organic chemistry whiz? We’re here to help out with some tips on interpreting IR specta! IR spectroscopy is a crucial component of organic chemistry, and mastering it will help you with everything from identifying functional groups and distinguishing between structural isomers to predicting reaction outcomes. First off, what is IR specta? It stands for infrared spectroscopy, which is a technique used to analyze the vibrations of molecules. By bombarding a sample with infrared radiation and analyzing how molecules absorb or reflect different frequencies of that radiation, you can get a lot of information about the chemical bonds and groups present in the sample. Now, how do you actually read an IR spectrum? Here are some general guidelines: - The x-axis represents the frequency of the infrared radiation (measured in wavenumbers, which is inversely proportional to wavelength). - The y-axis represents the percent transmittance or absorbance of the radiation. Some spectra display percent transmittance, which is the amount of radiation that passes through the sample relative to the amount that was initially sent through. Others show absorbance, which is the amount of radiation that was absorbed by the sample. - Peaks on the spectrum correspond to different types of bonds or groups in the sample. The position, intensity, and shape of the peaks can give you clues about what’s present. That may sound like a lot to keep track of, but fear not! We’ve got a handy guide to interpreting IR specta that breaks down the most important peaks and what they mean. Let’s get started! H2: O-H stretch (alcohols and carboxylic acids) If you see a peak around 3600-3200 cm^-1, that’s likely the O-H stretch from an alcohol or carboxylic acid. The peak can be broad or sharp depending on the molecule. IMG: (alt tag: peak at 3300 cm^-1) P: Here’s an example of an O-H stretch peak for ethanol: (H2O is also present in this spectrum as a result of hydrogen bonding, which causes a broad, intense peak around 3400 cm^-1.) H2: N-H stretch (amines) Amines can show a peak in the region of 3500-3100 cm^-1 for the N-H stretch. This peak is often broad and can overlap with other peaks. IMG: (alt tag: peak at 3300 cm^-1) P: Here’s an example of an N-H stretch peak for ethylamine: (Don’t be thrown off by the peak around 3300 cm^-1 – that’s actually the O-H stretch from impurities in the sample.) H2: C-H stretch (alkanes, alkenes, alkynes) This is a big one because C-H bonds are so common in organic molecules. The position of the peak depends on whether the bond is sp^3, sp^2, or sp hybridized (which affects the bond strength), as well as whether it’s in an alkane, alkene, or alkyne (which affects the bond shape and symmetry). For example, sp^3 C-H bonds in alkanes typically show a peak in the area of 3000-2800 cm^-1. Alkene C-H bonds tend to be higher in frequency (around 3100-3000 cm^-1), while alkyne C-H bonds are even higher (around 3300-3200 cm^-1). Keep in mind that other factors, such as the presence of functional groups and ring strain, can shift the position of C-H peaks. IMG: (alt tag: peak at 2920 cm^-1) P: Here’s an example of a C-H stretch peak for cyclohexane (an alkane): (Note that the peak around 3020 cm^-1 is due to an impurity in the sample.) Those are just a few examples of the peaks you might encounter in an IR spectrum. There are many more to learn about, including peaks for carbonyl groups, aromatic rings, and more. Remember, mastering IR specta is all about practice and familiarity with common functional groups and bond types. Keep studying those spectra and soon you’ll be an expert!
If you are looking for Most Commonly Used IR Spectroscopy Values In Organic Chemistry - The you’ve came to the right web. We have 5 Pictures about Most Commonly Used IR Spectroscopy Values In Organic Chemistry - The like How to read IR spectroscopy - Organic Chemistry Tutorials - YouTube, Interpreting IR Specta: A Quick Guide – Master Organic Chemistry and also How to read IR spectroscopy - Organic Chemistry Tutorials - YouTube. Here it is:
Most Commonly Used IR Spectroscopy Values In Organic Chemistry - The
 organicchemistoncall.comir spectroscopy
organicchemistoncall.comir spectroscopy
Interpreting IR Specta: A Quick Guide – Master Organic Chemistry
 www.pinterest.com.mxspectroscopy infrared interpreting hexanol carboxylic analyse specta mcat aromatic masterorganicchemistry alcohols hydrogen resonance
www.pinterest.com.mxspectroscopy infrared interpreting hexanol carboxylic analyse specta mcat aromatic masterorganicchemistry alcohols hydrogen resonance
Interpreting IR Specta: A Quick Guide – Master Organic Chemistry
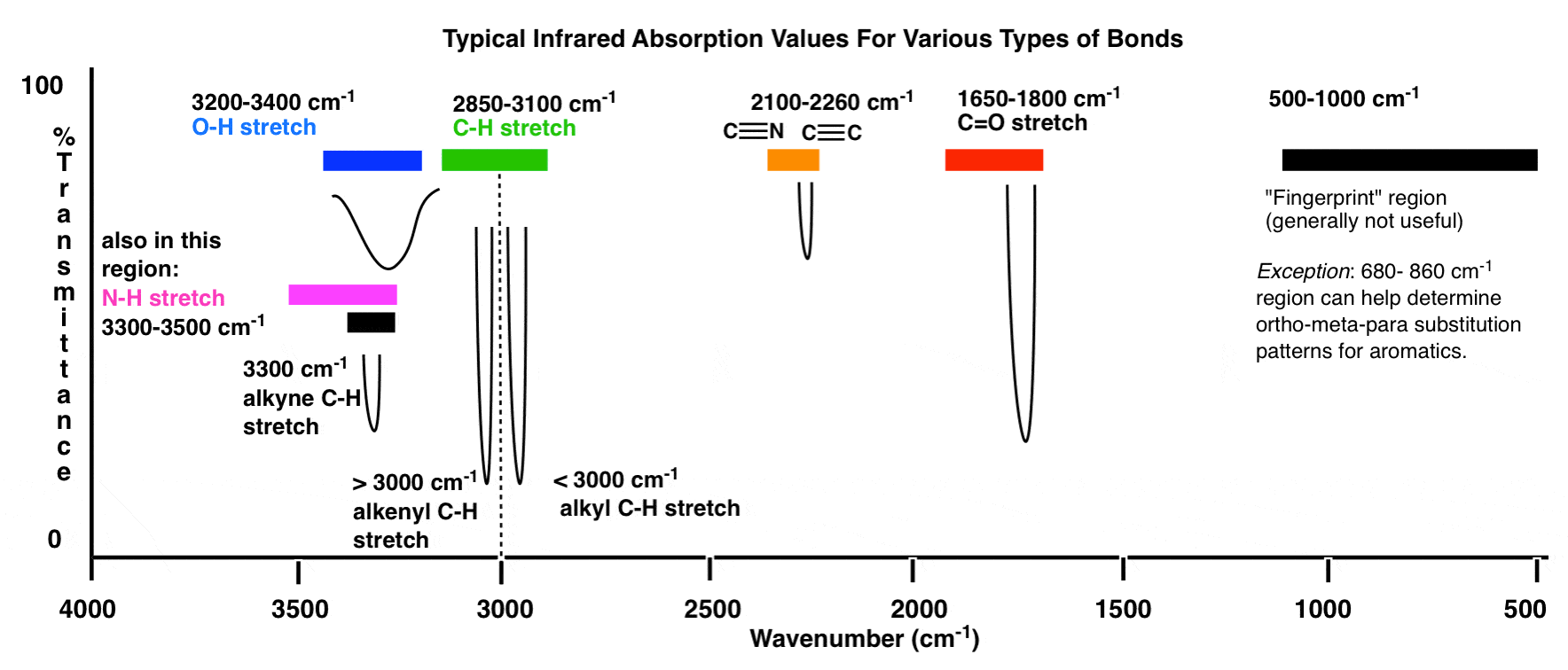 www.masterorganicchemistry.cominfrared spectrum spectroscopy absorption interpreting bonds ftir peaks absorptions specta acid
www.masterorganicchemistry.cominfrared spectrum spectroscopy absorption interpreting bonds ftir peaks absorptions specta acid
How To Read IR Spectroscopy - Organic Chemistry Tutorials - YouTube
 www.pinterest.caspectroscopy functional infrared compound chimie enseignement analyse chem biochemistry elcho
www.pinterest.caspectroscopy functional infrared compound chimie enseignement analyse chem biochemistry elcho
How To Memorize Ir Spectra - Memorize Dairy
 memorizedairy.blogspot.comspectroscopy infrared ftir interpreting pictorial interpretation nmr memorize chimie college analyse proton
memorizedairy.blogspot.comspectroscopy infrared ftir interpreting pictorial interpretation nmr memorize chimie college analyse proton
Spectroscopy infrared interpreting hexanol carboxylic analyse specta mcat aromatic masterorganicchemistry alcohols hydrogen resonance. Interpreting ir specta: a quick guide – master organic chemistry. Infrared spectrum spectroscopy absorption interpreting bonds ftir peaks absorptions specta acid